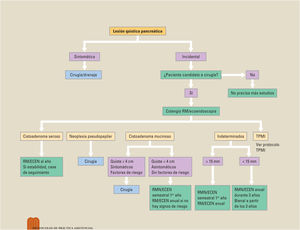
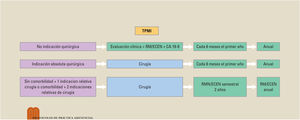
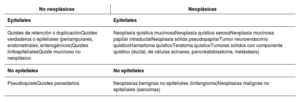
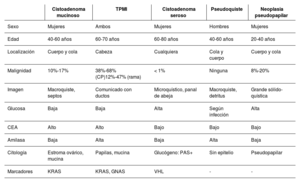
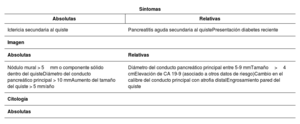
Las lesiones quísticas pancreáticas suelen ser un hallazgo incidental al realizar un estudio de imagen por otros motivos. El origen de estos quistes es variado y, según este, pueden ser benignas o tener potencial de malignidad; sin embargo, diferenciarlas no siempre es sencillo. Disponemos de varias herramientas para intentar identificar a qué tipo de quiste nos estamos enfrentando: ecoendoscopia, resonancia magnética, biomarcadores serológicos, quísticos e histológicos, pero no todos tienen una potencia diagnóstica óptima. A la hora de establecer el seguimiento, siempre debe tenerse en cuenta si el paciente tiene indicación quirúrgica; si es así, diferentes sociedades científicas han establecido estrategias de seguimiento y manejo de estas lesiones en función de la presencia de datos de riesgo de malignidad.
Palabras clave
Pancreatic cystic lesions are usually an incidental finding when performing an imaging study for other reasons. The origin of these cysts varies and, depending on their origin, they can be benign or potentially malignant. However, differentiating between the two is not always easy. Several tools are available to try to identify the type of cyst—endoscopic ultrasound; magnetic resonance imaging; and serological, cystic, and histological biomarkers—but not all of them have optimal diagnostic power. When determining follow-up, whether the patient has an indication for surgery must always be taken into account. If so, various scientific societies have established strategies for the follow-up and management of these lesions according to the presence of signs of malignancy risk.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h