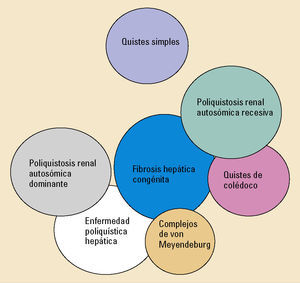
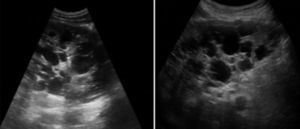
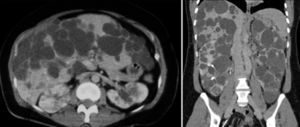
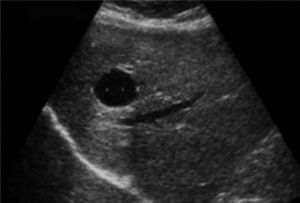
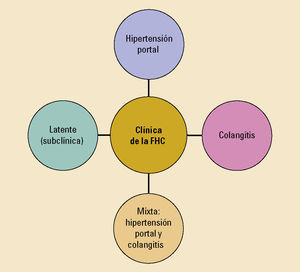
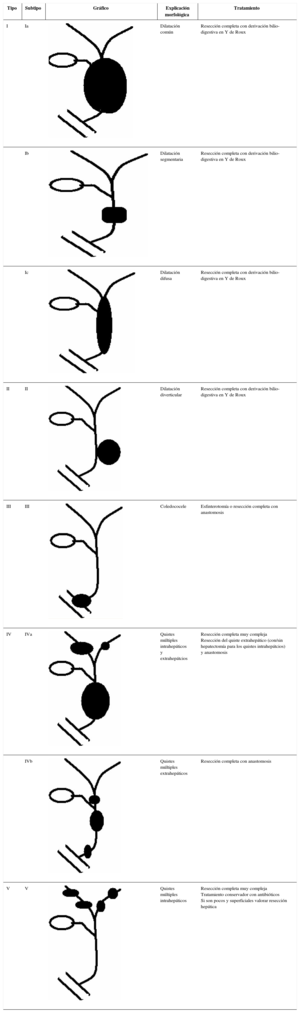
Las enfermedades fibropoliquísticas del hígado comprenden una serie de trastornos relacionados entre sí (figura 1). En cada uno de ellos se combinan diferentes grados de fibrosis con dilataciones quísticas del árbol biliar. El predominio y localización de cada uno de estos componentes difiere en función de cada enfermedad condicionando la presentación.
ClasificaciónLos trastornos son la enfermedad poliquística hepática, los quistes simples, la fibrosis hepática congénita, los complejos de von Meyendeburg, la enfermedad y el síndrome de Caroli y los quistes de colédoco. Aunque estos trastornos se expongan de forma aislada, la realidad es que existe un grado variable de superposición entre todos ellos desde el punto de vista patogénico, fisiopatológico y clínico. Se relacionan frecuentemente con trastornos de la misma índole a nivel renal.
PatogeniaSu origen es debido a malformaciones de la placa ductal durante el desarrollo embrionario que origina una proliferación excesiva del epitelio biliar. Como consecuencia aumenta la síntesis de matriz extracelular originando fibrosis y se forman grandes espacios quísticos llenos de líquido tanto en el parénquima hepático como en las vías biliares.
Palabras clave
Fibropolycistic diseases of the liver comprise a heterogeneous group of different disorders in which fibrosis is associated with segmental dilatations of the bile ducts. Although classified into specific conditions, there is much overlap between them and close association with fibrocystic anomalies in the kidneys is usually seen.
ClassificationIn polycystic liver disease associated with renal cysts the impairment in renal function may overshadow the liver disease. In congenital hepatic fibrosis the principal symptoms arise from portal hypertension, as the liver synthetic function is preserved. Simple hepatic cysts and von Meyendeburg complex are the minimal expression of all these fibrocystic diseases. Caroli¿s syndrome and Caroli¿s disease both have large intrahepatic bile duct dilatations; however liver fibrosis and portal hypertension signs occur only in Caroli¿s syndrome. Dilatation of the extrahepatic bile ducts, name commonly as choledocal cysts cause cholangitis.
PathogenyThe origin of all these conditions is the malformation of the ductal plate during the embryonic period. On the one hand, the abnormal proliferation of the bile epithelium leads to an excess synthesis of extracellular matrix (fibrosis). On the other hand large cysts arise in the liver and also in the bile tree.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h