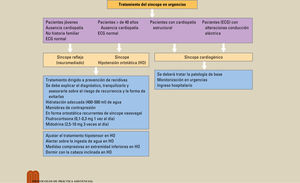
El síncope puede clasificarse en reflejo (neuromediado), por hipotensión ortostática o secundario a patología cardiovascular. Dado que el síncope reflejo tiene buen pronóstico, el tratamiento va dirigido básicamente a la prevención de recidivas. Se debe explicar a todo paciente el diagnóstico, tranquilizarlo y asesorarle sobre el riesgo de recurrencia y la forma de evitar las situaciones y los factores desencadenantes. Las maniobras isométricas de contrapresión de miembros superiores e inferiores pueden evitar el desarrollo de síncope una vez iniciados los síntomas y evitando caídas. Puede considerarse el entrenamiento con basculación para instruir a los pacientes jóvenes. En pacientes con episodios muy recurrentes de la forma ortostática del síncope vasovagal, puede considerarse la administración de fludrocortisona o midodrina. El síncope por hipotensión ortostática se suele presentar en pacientes de edad y con tratamiento hipotensor. Debemos, en primer lugar, ajustar el tratamiento hipotensor. La ingesta de 400-500ml de agua entre 3-4 veces al día puede ayudar en ambos síncopes reflejo y por hipotensión ortostática. El síncope cardiogénico se presenta en pacientes con cardiopatía de base o electrocardiograma anormal, suele tener peor pronóstico y debe conocerse su mecanismo final para establecer el tratamiento.
Palabras clave
Syncope can be classified as reflex (neuromediated) syncope, syncope due to orthostatic hypertension, or syncope secondary to cardiovascular pathology. Given that reflex syncope has a good prognosis, treatment is essentially aimed at preventing recurrence. The diagnosis must be explained to all patients and they must be reassured and advised on the risk of recurrence and how to avoid triggering situations and factors. Isometric counterpressure movements in the upper and lower limbs can avoid onset of syncope once symptoms have begun as well as prevent falls. Tilt training can be considered for instructing young patients. In patients with very recurrent episodes of the orthostatic form of vasovagal syncope, administration of fludrocortisone or midodrine can be considered. Syncope due to orthostatic hypotension tends to occur in elderly patients and those with hypotensive treatment. We must first adjust hypotensive treatment. Intake of 400 - 500ml of water three to four times per day can help in both reflex and orthostatic hypotension syncope. Cardiogenic syncope occurs in patients with underlying cardiopathy or an abnormal electrocardiogram. It tends to have a poor prognosis and its end mechanism must be understood in order to establish treatment.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h