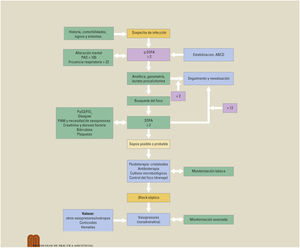
El paciente séptico con inestabilidad hemodinámica requiere una actuación rápida.
EpidemiologiaSu frecuencia está aumentando por las sobreinfecciones intrahospitalarias.
EtiologíaCualquier foco infeccioso puede producir una sepsis con inestabilidad hemodinámica.
Manifestaciones clínicasSerán las derivadas de la infección y las de las disfunciones orgánicas.
Diagnóstico. De sospecha con qSOFA y completar con pruebas de laboratorio y de imagen.
PronósticoLa actuación precoz disminuye su mortalidad de forma significativa.
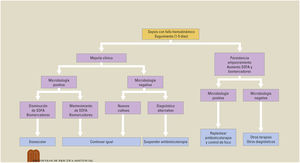
TratamientoAntibioterapia precoz, fluidoterapia con cristaloides y drenaje del foco. Si no es suficiente se añadirán vasopresores y se monitorizará hemodinámicamente. Debe realizarse un seguimiento clínico apoyado en la escala SOFA y en biomarcadores para reevaluar o desescalar el tratamiento.
Palabras clave
Septic patient with hemodynamic instability need early diagnosis and treatment.
EpidemiologyIts frequency is increasing by hospital infections.
EtiologyAny infectious source may produce a septic condition with hemodynamic instability.
Clinical manifestationsThose derived from infection and those derived from organic dysfunctions.
DiagnosisqSOFA scale for suspicion. After It will then be completed with laboratory and imaging tests.
PrognosisEarly intervention decreases mortality significantly.
TreatmentEarly antibiotic therapy, crystalloid fluid therapy and drainage of the source. If these arenot enough, vasopressors and advanced hemodynamic monitoring will be required. A clinical follow-up based on the SOFA scale and on biomarkers should be performed to re-evaluate or de-escalate the treatment.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h