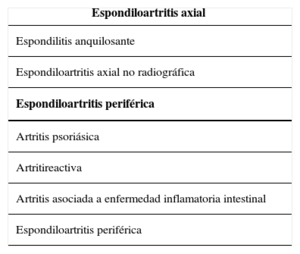
Las espondiloartritis comprenden un conjunto de enfermedades que comparten en gran medida sus características clínicas y su etiopatogenia. Las enfermedades que pertenecen a este grupo son la espondilitis anquilosante, la espondiloartritis axial no radiográfica, la espondiloartritis periférica, la artritis psoriásica, la artritis reactiva y la asociada a enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII).
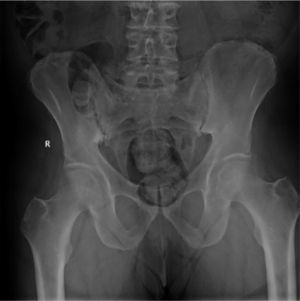
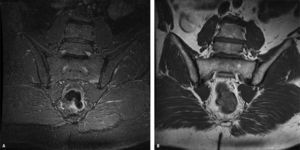
Patogénesis y manifestaciones clínicasEn su patogenia se ven implicados varios factores, como la microbioma intestinal, el HLA-B27 y el eje IL23-IL17. Generalmente comienzan con dolor axial inflamatorio y/u oligoartritis de miembros inferiores, junto con dactilitis y entesitis. La manifestación extraarticular más frecuente es la uveítis.
Criterios de clasificaciónExisten unos nuevos criterios clasificatorios desarrollados por el grupo ASAS para poder realizar un diagnóstico y tratamiento precoz de estos pacientes, mejorando de esta manera la calidad de vida, la rigidez matutina y el dolor articular.
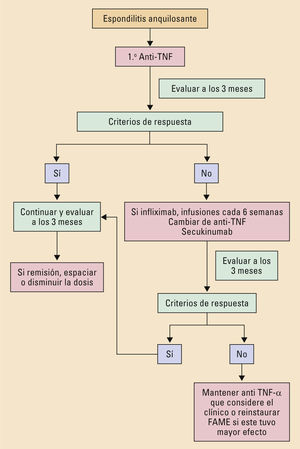
TratamientoEl tratamiento debe realizarse de forma escalonada, comenzando con los antiinflamatorios no esteroideos. Según la respuesta y la afectación del paciente, se pueden emplear fármacos modificadores de enfermedad, infiltraciones articulares y fármacos biológicos como los antifactor de necrosis tumoral y secukinumab. El tratamiento no farmacológico con fisioterapia y el abandono del hábito tabáquico deben recomendarse en todos los pacientes.
Palabras clave
Spondyloarthritis (Spa) is the term used to describe patients with similar clinical features. There are ankylosing spondylitis, non-radiographic axial SpA (nr-axSpA), peripheral SpA, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis and arthritis associated with gastrointestinal disease.
Pathogenesis and clinical manifestationsIn the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis are involved gut microbiome, HLAB27 and the axis interleukin 23-interleukin 17. Patients with Spa have usually chronic inflammatory back pain, oligoarthritis in the lower extremities, dactylitis and enthesitis. Uveitis is the most frequent non-musculoskeletal disease.
Classification criteriaThere are new classification criteria developed by the Assessment of Spondiloarthritis International Society (ASSAS). It allows us to make a diagnosis and early treatment of these patients, thus improving the quality of life, the morning stiffness and pain.
TreatmentThe treatment should be phased, starting with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. According to the response, and the involvement of the patient, disease modifying drugs, infiltrations articular and biological agents may be used. Non-pharmacological treatment with physiotherapy and the abandonment of the smoking habit should be recommended in all patients.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h